

Sample in statistics: What it is, how to find it.Ĭheck out our statistics YouTube channel. If you aren’t sure if you have a sample or a population, read these articles: Many measures of dispersion (like the variance) have two different formulas, one for a population and one for a sample. Warning: When using a calculator (or a formula), check to make sure you are using the correct setting (or formula) for your data. The figure for data set B is exactly ten times that of A. For example, take a look at the standard deviations for the two data sets: In fact, nearly all measures of dispersion would be ten times greater for data set B, which makes sense as the range is ten times larger. However, the range (which gives you an idea of how spread out the entire set of data is) is much larger for data set B (60) when compared to data set A (6). By looking at the data sets you can probably tell that the means and medians are the same (100) which technically are called “measures of central tendency” in statistics. Let’s say you were asked to compare measures of dispersion for two data sets. High dispersion is associated with low precision. In some processes, like manufacturing or measurement, low dispersion is associated with high precision.
Interdecile range: the difference between the first decile (10%) and the last decile (90%).Interquartile range (IQR): describes where the bulk of the data lies (the “ middle fifty” percent).Index of Dispersion: a measure of dispersion commonly used with nominal variables.It tells you how spread out numbers are from the mean, Standard deviation: probably the most common measure.Coefficient of dispersion: A “catch-all” term for a variety of formulas, including distance between quartiles.
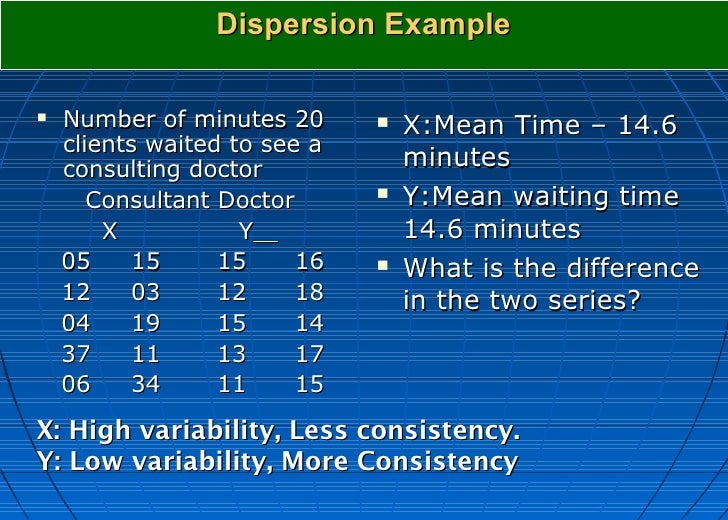
Image: Seton Hall University Measures of Dispersion. The larger the box, the more dispersion in a set of data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
